DataPoints - National Data Commissioner Update December 2023
Here’s our wrap on the year. There’s a lot to celebrate.
Accrediting the first data users
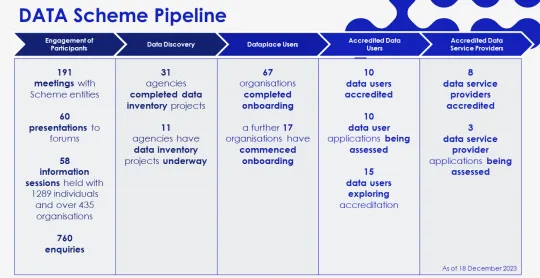
A big milestone for the Scheme was accrediting the first data users. Hot off the press! In the last few weeks we’ve accredited 2 more data users - the University of Sydney and Monash University, taking the total to 10. We’ve also recently added the Department of Health WA as an accredited data service provider, taking the total to 8. Check out the full list of accredited entities here.
Supporting the National Disability Data Asset and other sharing
We’ve invested in supporting eligible participants to use the DATA Scheme with good progress made on the National Disability Data Asset – an initiative of all Australian Governments working with the disability community that will help support people with disability, their carers and the community. We are looking forward to seeing sharing under the Scheme in 2024.
We’re supporting Scheme participants to share under the DATA Scheme by answering their questions and adding to our bank of guidance. The newest addition is our Guide to Registering Data Sharing Agreements, which you can find here. We’ve updated our guidance on when sharing of data is barred under the DATA Scheme and released draft guidance on the Charging of fees by Accredited Data Service Providers for public consultation. Please provide your feedback by 19 January 2024.
Enhancing Dataplace services and onboarding agencies
Dataplace is the digital platform for Scheme participants and others to manage their data requests and sharing agreements. There are now 67 organisations onboarded - more than double the number onboarded this time last year. We’ve rolled out more services on Dataplace and will continue to improve and extend these in 2024, including by integrating it with the Australian Government Data Catalogue.
Engaging and educating DATA Scheme participants
This year we have helped 24 Australian Government agencies develop their data inventories, taking the total to 31, with an additional 11 underway. We’ve also published guidance on developing a data inventory and metadata attributes. In the new year, we will begin to extend our education offering beyond data inventories to other aspects of data maturity.
Our webinar Wednesdays will return next year starting in February. Keep an eye on our website to register.
The next DataPoints will be in February. Keep in touch by following us on LinkedIn or you can contact us on our website.
Until then, best wishes for the holidays and the new year!
Gayle



